- Email: info@swarupeye.com
- Hyderabad
- Call: +918886309030
Mon-Sat 09:00AM-07:00PM
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions, can have a significant impact on various parts of the body, including your eyes. At Swarup Eye Centre, we understand the importance of diabetic eye care and are dedicated to helping you maintain clear vision for years to come.
The Diabetic-Eye Connection: Why Regular Checkups Matter
High blood sugar levels can damage the delicate blood vessels in your retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye. This damage can lead to a condition called diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness.
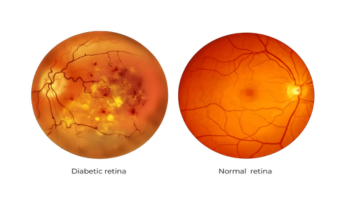
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
- Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition caused by diabetes damaging the blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye), potentially leading to vision loss or blindness if left untreated.
- Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high blood sugar levels, characteristic of diabetes, damage the small blood vessels in the retina. In later stages of the disease, blood vessels in the retina start to bleed into the vitreous (gel-like fluid that fills your eye). If this happens, you may see dark, floating spots or streaks that look like cobwebs.
Time Guidelines for Diabetic Patients to Have an Eye Checkup
Type 1 Diabetes:
- It's generally recommended that people with type 1 diabetes have their first dilated eye exam within five years of their diagnosis.
- After the initial exam, annual eye exams are typically advised.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Because type 2 diabetes may be present for some time before diagnosis, it's recommended that individuals have their first dilated eye exam at the time of diagnosis.
- Following the initial exam, annual eye exams are generally recommended.
Pregnancy:
- Women with diabetes who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should have a comprehensive eye exam during the first trimester.
- They should also be closely monitored during pregnancy and for up to one year postpartum, as pregnancy can exacerbate diabetic retinopathy.
Frequency Adjustments:
- The frequency of eye exams may be adjusted based on the presence and severity of diabetic retinopathy or other eye conditions.
- Your eye doctor will provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs.
Causes, Symptoms, and Stages
Causes:
- The main cause is high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes, which can lead to the blood vessels in the retina to swell, leak fluid, and even close off.
Symptoms:
- In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any noticeable symptoms, but as the disease progresses, you may experience:
- Blurry vision
- Floaters
- Dark or empty spots in your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night, and even vision loss
Stages:
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through different stages:
- Non Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: In this stage, blood vessels may swell, bulge, or leak into the retina.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: In the more advanced stages, the body may try to grow new blood vessels, but these vessels are often fragile and can bleed into the vitreous humor (the gel-like substance that fills the eye), leading to floaters, blurry vision, or even vision loss.
Risk Factors and Diagnosis
Risk Factors:
- People with diabetes are at risk, and the longer someone has diabetes, the greater the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Other risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, and poor blood sugar control.
Diagnosis:
- Diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed through a comprehensive dilated eye exam.
- This allows our ophthalmologist to look through a special lens to see the inside of your eye.
- Our doctor may do Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) to look closely at the retina. A machine scans the retina and provides detailed images of its thickness. This helps our doctor find and measure swelling of your macula.
- Fluorescein Angiography: A diagnostic procedure that uses a special dye to visualize blood flow in the retinal vessels.
- Ultra wide view Fundus photography: High-resolution wide view images of your retina allow us to detect even subtle changes in blood vessels.
Treatment
The Swarup Eye Centre offers several treatments for diabetic retinopathy:
- Injections: We inject medication (anti-VEGF) directly into the eye as a treatment to help stop the growth of new blood vessels. The injections work to block the growth signals and subsequently the generation of new blood vessels, it also makes the blood vessels leak less.
- Laser Therapy: This is an effective form of treatment. It is more commonly used in patients who have more advanced symptoms of diabetic retinopathy.
- Focal Laser Therapy: This procedure is performed in order to reduce the amount of fluid or blood leaking in the eye. The Focal Laser Therapy works by stimulating the retinal pigment epithelium to pump fluid out, and laser the protrusions in the blood vessels to prevent leakage.
- Scatter Laser: This treatment is again administered by laser in the peripheral retina which causes the abnormal new blood vessels to shrink in size.
- Eye Surgery (Vitrectomy Surgery): This treatment is recommended in patients who have advanced diabetic retinopathy and where other possible laser treatments will not be effective on their own.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
Managing your diabetes is the best way to lower your risk. This includes controlling your blood sugar level, blood pressure, and cholesterol, along with regular diabetes and eye checkups. - Is laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy painful?
Most patients experience little to no discomfort during laser treatment. You may feel a sharp prick or a sensation of pressure in the eye. The eye is usually numbed before treatment. - How often should someone with diabetes get an eye exam?
If you have diabetes, it's recommended to have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. More frequent medical eye exams may be necessary if you have diabetic retinopathy or if your eye doctor advises it. - Can vision loss from diabetic retinopathy be reversed?
Unfortunately, loss of vision from diabetic retinopathy is often irreversible. However, early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of blindness and can sometimes restore vision that has been lost.
